TOGAF Core Concepts
TOGAF Core Concepts
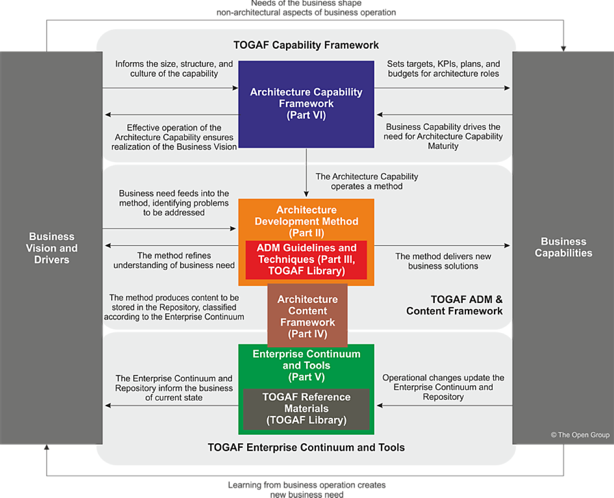
TOGAF is structured to reflect - in terms of structure and content - an Enterprise Architecture capability within an organization.
This post will cover the structure of the TOGAF standard. And a brief summary of each part content.
TOGAF Part I is an introduction to TOGAF and enterprise architecture and definitely should read it!. "Part I" will not be covered in this article.
Part II - Architecture Development Method
The TOGAF Architecture Development Method or ADM is the result of continuous contributions from a large number of architecture practitioners. It describes a method for developing and managing the life-cycle of an Enterprise Architecture, and forms the core of the TOGAF standard.
The application of the TOGAF ADM is supported by an extended set of resources, guidelines, templates, checklists, and other detailed materials:
- Part III: ADM Guidelines & Techniques
- White Papers and Guides published by The Open Group, classified and referenced in the TOGAF Library
Some Key points to understand ADM:
-
The ADM is iterative.
For each Iteration architects decide, breadth, level of detail, architectural assets to be leveraged.
-
ADM is generic.
As a generic method it may be tailored to specific needs, like the organization, the iteration, level of maturity, etc.
Part III - ADM Guidelines and techniques
- Guidelines for Adapting the ADM Process
- Applying Iteration to the ADM
- Applying the ADM across the Architecture Landscape
- Techniques for Architecture Development
- Architecture Principles
- Stakeholder Management
- Architecture Patterns
- Gap Analysis
- Migration Planning Techniques
- Interoperability Requirements
- Business Transformation Readiness Assessment
- Risk Management
- Capability-Based Planning
- Using the TOGAF Framework with Different Architectural Styles
- Integrating Risk and Security within a TOGAF® Enterprise Architecture
- TOGAF® Series Guide: Using the TOGAF® Framework to Define and Govern Service-Oriented Architectures
- Digital / IoT Guidelines
- Cloud Computing Guidelines
- Guidelines developed collaboratively with other bodies
Part IV - Architecture Content Framework
Architects executing the Architecture Development Method (ADM) will produce a number of outputs as a result of their efforts. The content framework provides a structural model for architectural content.
Content Framework consists of:
- Content Metamodel
- Architectural artifacts
- View/Viewpoints
- Catalog
- Matrix
- Diagram
- Architectural deliverables
- Building blocks
Part V - Enterprise Continuum & Tools
The Enterprise Continuum describes a view of the Architecture Repository that provides methods for classifying architecture and solution artifacts, showing how the different types of artifact evolve, and how they can be leveraged and re-used.
Architecture Partitioning describes the various characteristics that can be applied to classify and then partition architectures
The Architecture Repository shows how the abstract classifications of architecture can be applied to a repository structure so that architectures can be organized and easily accessed
Tools for Architecture Development provides guidelines on selecting a tool set to create and manage architectural artifacts
Part VI - Reference Models
Reference models section has been removed from TOGAF 9.2. this corresponds to TOGAF 9.1.
A reference model should meet the following criteria
- Abstract
- Entities and relationships
- Within an environment
- Technology agnostic
Reference models examples
- Core Architecture Data Model reference model of DoDAF
- Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework reference model of the FEA
- HP Information Security Service Management (ISSM) - Reference Model (RM)
- IBM Information Framework, a reference model for financial services.
- ISA-95, ISA-88
Technical Reference Model (TRM)
TRM focuses on the Application Platform space.
Integrated Information Infrastructure Reference Model (III-RM)
The III-RM is a subset of the TOGAF TRM in terms of its overall scope. III-RM address the need to design an integrated information infrastructure to enable Boundary less Information Flow.
Part VII - Architecture Capability Framework
In order to successfully operate an architecture function within an enterprise, it is necessary to put in place appropriate organization structures, processes, roles, responsibilities, and skills to realize the Architecture Capability.
The Architecture Capability Framework provides a set of reference materials for how to establish such an architecture function.
TOGAF uses ADM to establish an Architecture Capability
TOGAF Architecture Capability Framework provides as well guidelines for:
- Architecture Board
- Architecture Compliance
- Architecture Contracts
- Architecture Governance
- Architecture Maturity Models
- Architecture Skills Framework
Conclusion
With this we conclude this quick summary of TOGAF 9 content and structure. As the reader can see TOGAF is much more than the ADM, as it provides a rich set of guidelines, techniques and frameworks for content and architecture capabilities.
That's all folks! Gonzalo Sáenz